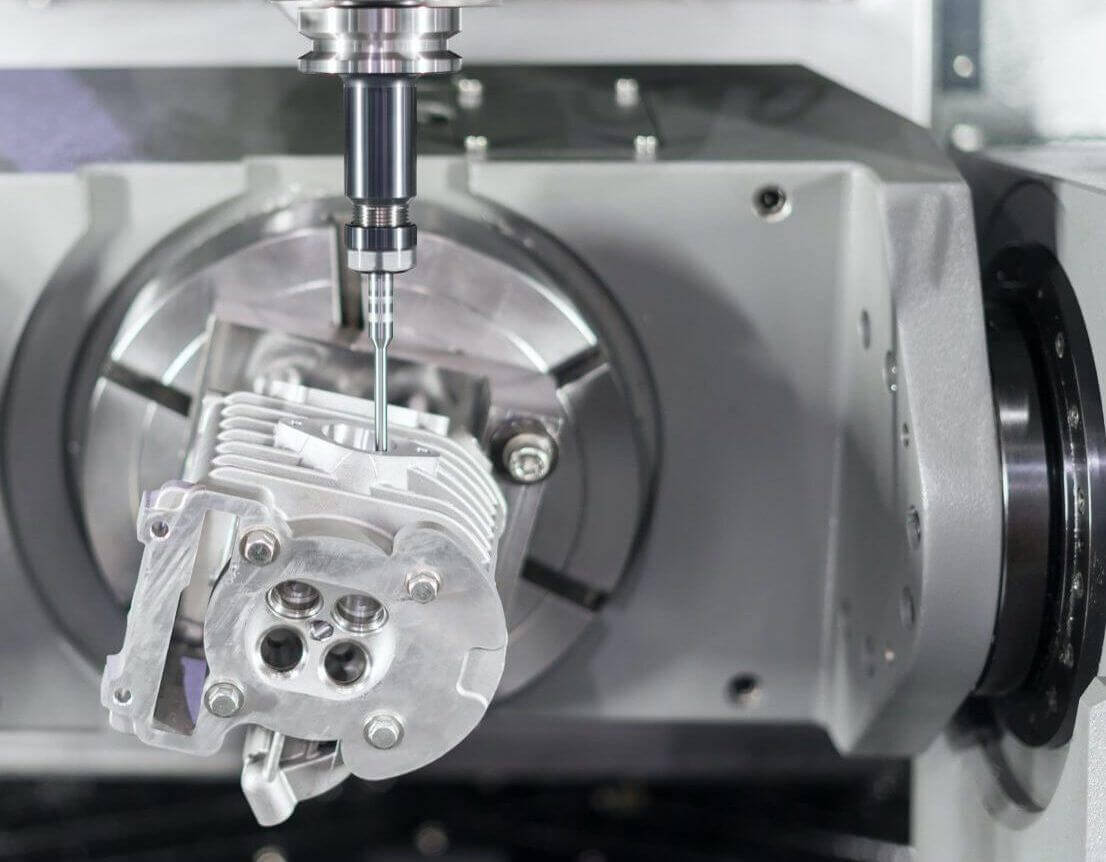
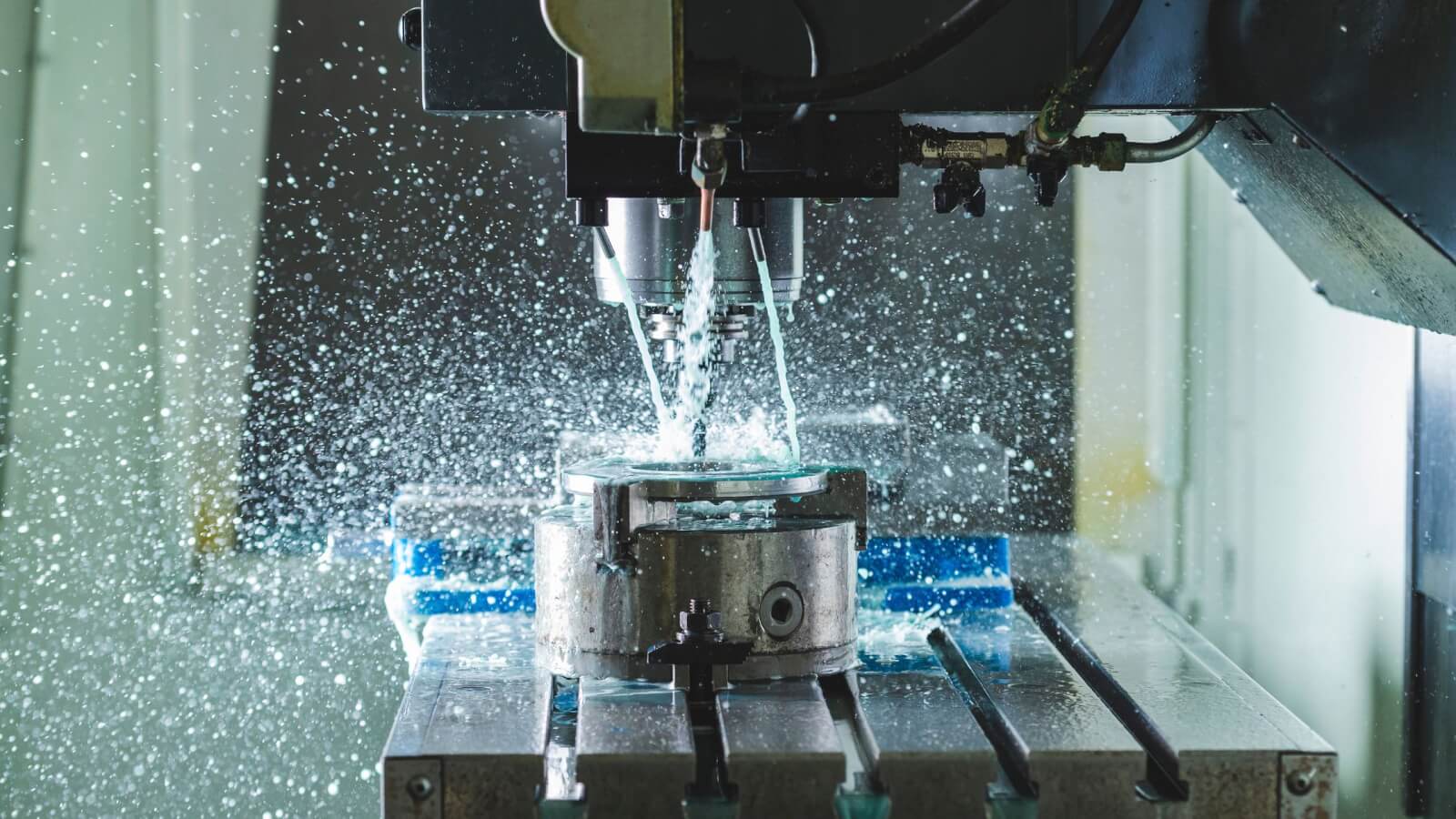
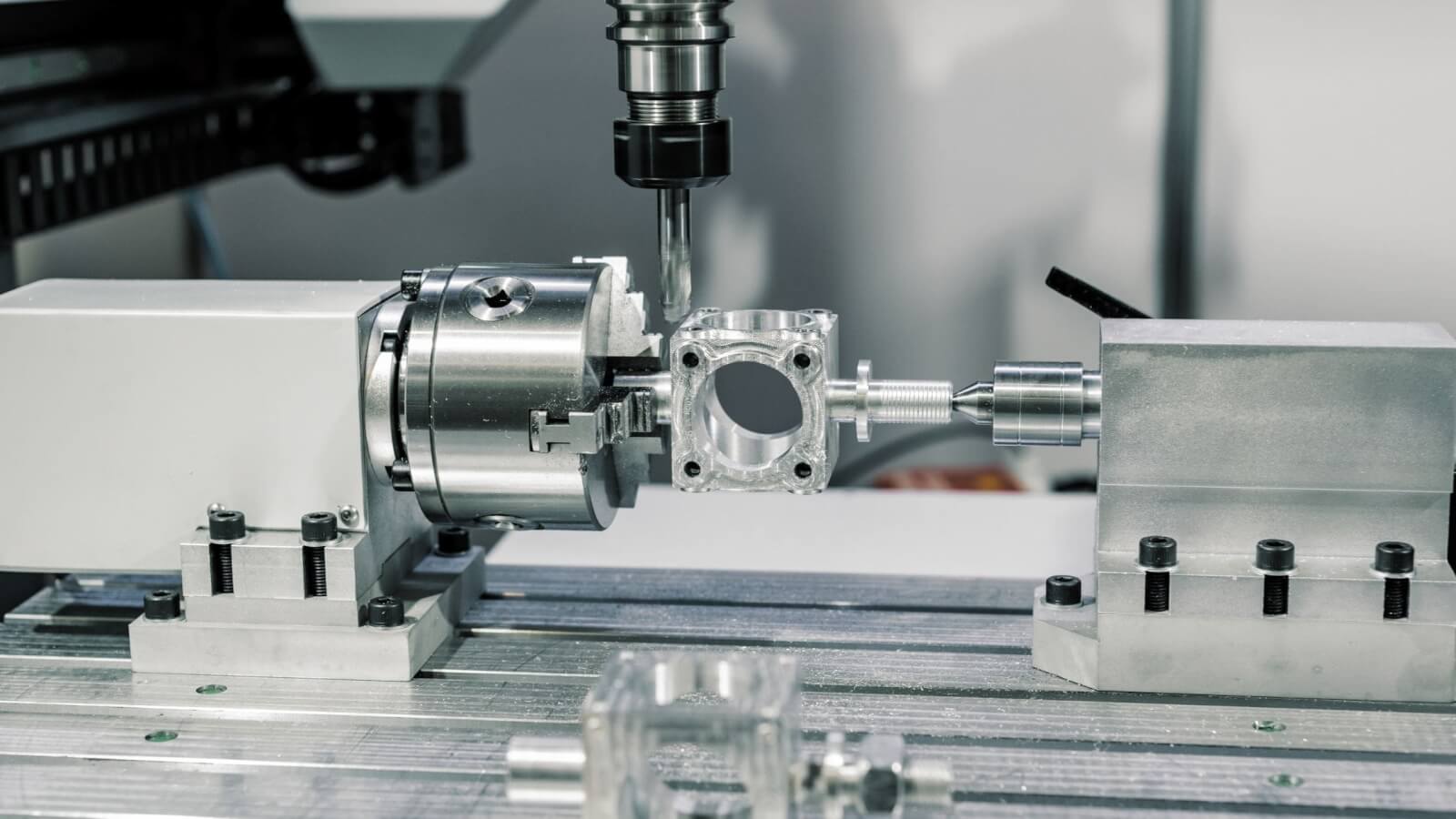
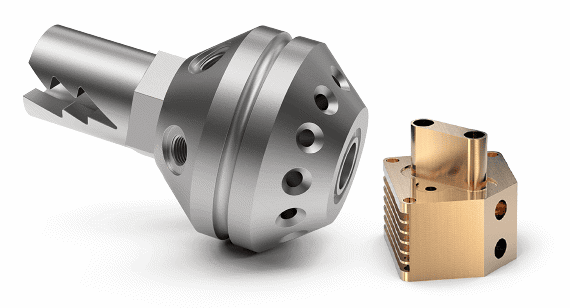
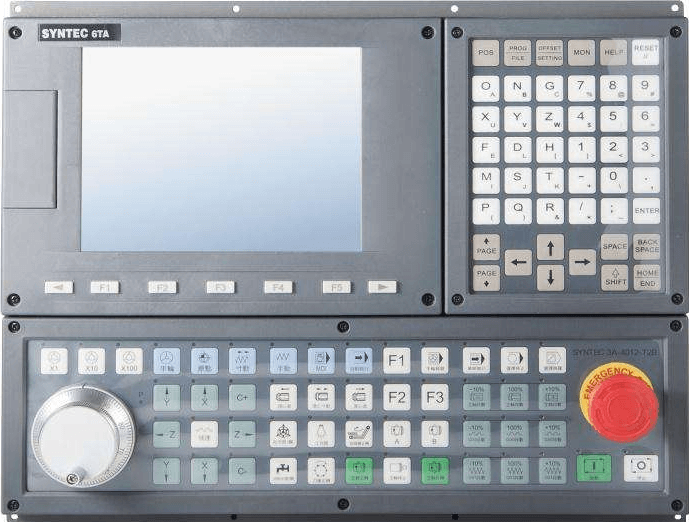
CNC milling machines have revolutionized manufacturing, enabling the creation of complex parts with unprecedented precision. But what makes these machines tick, and how do they achieve such remarkable accuracy in producing CNC milling parts?
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of CNC milling, exploring the core components, axes, tools, and support systems that work together to bring raw material to life as a perfectly machined part. Are you ready to uncover the secrets of precision machining and CNC milling parts?
Key Takeaways
- CNC milling is a complex CNC machining process involving various components that work together to create precise parts with desired surface finishes.
- The CNC controller, column and base structure, power feed mechanism, axes and tools are all essential for achieving accuracy and precision in the machining operations.
- CNC vs manual machining depends on complexity of project. From raw material to finished part requires programmed cutting tools & core components.
Exploring the Core Components of a CNC Mill
A CNC milling machine is a marvel of engineering, combining various components to transform raw material into intricate shapes and designs. The machine control unit (MCU) is pivotal in managing the machine’s movements and operations, while the core components function in unison to enable efficient operation and accurate cnc machine work capabilities.
CNC mills consist of several main components, including:
- CNC controller
- Column and base structure
- Power feed mechanism
- Tool changer
- Work table and T-slots
- Spindle and servo motors
- Display unit and control panel
These parts collaborate to ensure precise milling operations, turning raw material into custom parts with the required surface finishes.
The Heart of the Machine: CNC Controller
Acting as the machine’s brain, the CNC controller performs several important functions:
- Interprets G-code instructions
- Manages the mill’s motions and operations
- Translates input into corresponding machine movements
- Executes commands by dispatching appropriate signals to the stepper and servo motors.
The machine control unit (MCU) is a critical component of a CNC milling machine. It performs several important functions, including:
- Regulating the movements and operations of the mill in accordance with the G-code instructions
- Interpreting G-code coordinates into movements executed by servo motors along the machine axes
- Controlling tool changers and coolant activation
- Interpreting feedback from sensors to verify the tool’s position after the movement is completed
The MCU plays a crucial role in ensuring precise milling operations.
The Backbone: Column and Base Structure
The column and base structure provide the support and stability necessary for accurate and consistent machining. These structures are typically constructed from materials such as epoxy-granite, cast iron, or aluminum, which offer the required strength and rigidity.
The column and base structure’s design contributes significantly to CNC mill precision by minimizing vibrations and deflections during machining, thus ensuring cuts of high precision and accuracy. Moreover, the weight distribution of the machine is affected by the design of the column and base structure, further enhancing its stability and precision.
The Mover: Power Feed Mechanism
The power feed mechanism ensures the workpiece and cutting tool move precisely along the machine’s axes, thereby enabling accurate cutting operations. This mechanism is composed of:
- The knee
- The driving system
- The bed
- T-slots
All working together to regulate the vertical, longitudinal, and transverse feeds of the machine, including the use of a vertical positioning screw.
While conventional CNC machine beds feature motion along the horizontal X- and Y-axes, advanced 5-axis machine beds can incorporate rotational motions along the X- and Y-axes for even more precise control. This versatility enables CNC machines to tackle a wide range of cutting and shaping tasks, resulting in highly accurate and intricate machined parts.
Precision in Motion: Axes and Their Importance
The X, Y, and Z-axes in a CNC milling machine control the cutting tool and workpiece’s movement, enabling machining of high precision and accuracy. Understanding the importance of these axes in CNC milling machines is crucial for realizing the full potential of these powerful tools.
The different axes in milling are:
- The Z-axis controls the vertical movement of the cutting tool or workpiece, providing precise positioning and depth control during the milling process.
- The X-axis allows for movement from left to right and vice versa, parallel to the cutting tool.
- The Y-axis governs the vertical movement of the part.
The combination of these three axes enables the CNC machine to fabricate intricate shapes and contours in the material, resulting in precise and accurate machined components.
Achieving Depth: The Role of the Z-Axis
In CNC milling, the Z-axis significantly affects the depth of the cut. It regulates the vertical motion of the tool, thereby providing accurate control over the depth of the machining operation. By interacting with the X and Y axes, the Z-axis enables the creation of complex three-dimensional parts with high levels of precision.
Issues with the Z-axis, such as movement irregularities or discrepancies in determining depth, can be remedied by inspecting the control card for looseness or malfunction, troubleshooting the coordinate determination process, or checking for binding or slipping. By ensuring the precision of the Z-axis, CNC mills can achieve optimal depth control, enabling the creation of intricate and detailed parts.
Lateral Dynamics: Understanding the X and Y Axes
The X and Y axes govern the cutting tool and workpiece’s lateral movement, facilitating accurate and uniform machining across the material’s surface. The X-axis denotes the movement from left to right or vice versa, parallel to the cutting tool, while the Y-axis denotes the movement from front to back. Collectively, these axes dictate the precise positioning and movement of the cutting tool, facilitating accurate and controlled machining of the material’s surface.
The CNC controller coordinates with motors and drive components to facilitate the movement of the X and Y axes, allowing for precise control over the cutting tool’s position and movement during the milling process. This accurate control ensures that the machined parts are consistent and meet the desired specifications.
The Cutting Edge: Tools and Attachments
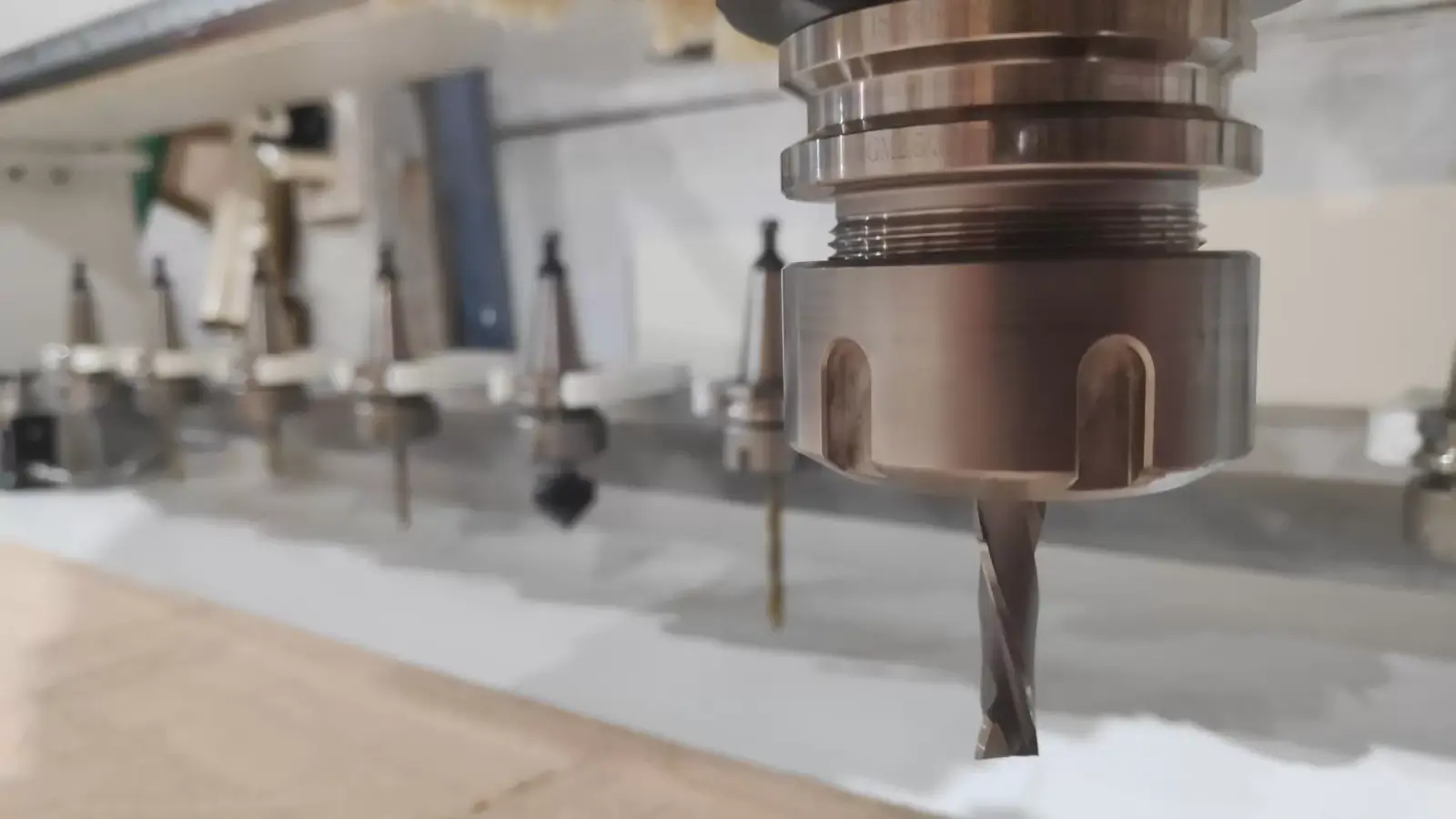

Choosing the right milling tool is key to ensuring high performance and quality in machined parts. Additionally, coolant systems help extend tool life and improve surface finishes by reducing heat and friction during the milling process. By understanding the roles and functions of these various tools and attachments, operators can optimize their CNC milling machines for maximum precision and accuracy.
The Versatile Tool Changer
In CNC milling machines, the tool changer facilitates seamless switching between different cutting tools during the milling process, eliminating the need to stop the machine. This feature enables multiple machining operations to be performed in a single setup, greatly improving efficiency and production capacity.
Various types of tool changers are available to suit different milling operations and machining needs. These include:
- Automatic tool changers with chain magazine
- Turret head type
- Drum-type ATC
- Disc-type ATCs
By incorporating a versatile tool changer into the CNC milling process, operators can achieve a wide range of tasks with ease and precision, including the use of CNC routers.
Extending Tool Life with Coolant Systems
In CNC milling, coolant systems assist in prolonging the life of cutting tools and enhancing the machined parts’ surface finish by reducing heat and friction during machining. By maintaining optimal cutting temperatures and lubricating the cutting tool, coolant systems minimize wear on the tool and workpiece, ultimately enhancing machining efficiency and extending tool life.
When selecting a coolant for CNC milling, factors such as:
- Material compatibility
- Tooling requirements
- Cutting conditions
- Corrosion protection
- Tool life extension
- Cost
should all be taken into account. By carefully choosing and employing the right coolant system, operators can significantly improve the performance and longevity of their cutting tools and achieve better surface finishes on machined parts.
The Support Cast: Secondary but Essential Parts
Besides the primary components, a CNC milling machine necessitates secondary yet crucial parts that control the cutting tool’s movement, support the arbor, and secure the workpiece during machining. These components, such as servo motors, ball screws, and linear guides, work together with the main components to ensure the machine operates effectively and efficiently.
These secondary components may not be as prominent as the core parts of a CNC mill, but they play a crucial role in achieving the desired precision and accuracy in the final machined product. By understanding the importance of these components and how they contribute to the overall performance of the CNC milling machine, operators can optimize their machines for maximum precision and effectiveness.
The Stage for Materials: Work Table and T-Slots
By providing a stable platform for securing the workpiece during machining, the work table and T-slots ensure results of high accuracy and consistency. The work table is typically constructed from durable materials like aluminum or cast iron, providing a reliable surface for securing workpieces during the milling process.
T-slots are integral for fixturing and workholding, designed to work with T-nuts for secure clamping and positioning of workpieces during machining. T-slots offer flexibility and versatility in holding various fixtures and accessories, simplifying the setup and securing of workpieces for accurate milling.
By providing a stable platform for materials, the work table and T-slots ensure the precision and accuracy of the CNC milling process.
The Driving Force: Spindle and Servo Motors
The spindle and servo motors are responsible for propelling the cutting tool and governing its movement along the machine’s axes, which allows for precise and efficient machining operations. The spindle motor provides the torque, speed, and accuracy needed for precise cutting and machining, while the servo motor controls the precise position of mechanical components by receiving electrical signals and translating them into movement.
By ensuring the proper functioning of the spindle and servo motors, operators can achieve optimal performance and precision in their CNC milling machines. These motors play a critical role in driving the cutting tool and controlling its movement during the milling process, resulting in highly accurate and intricate machined parts.
Enhancing Precision: Feedback and Control Systems
Feedback and control systems serve to enhance the accuracy and precision of CNC milling machines. These systems include position feedback systems, speed feedback systems, and adaptive control systems, which work together to verify and adjust the precise position of a mechanical component during the milling process.
By incorporating these feedback and control systems into their CNC milling machines, operators can ensure that the machine maintains optimal performance and precision throughout the machining process. These systems play a crucial role in achieving the desired level of accuracy and consistency in the final machined product, making them an essential component of any CNC milling operation.
The Eyes of the Machine: Display Unit and Control Panel
Acting as the main interface between the operator and the CNC milling machine, the display unit and control panel enable the monitoring and control of the machine’s operations. The display unit provides the operator with essential information on the machine’s status, while the control panel enables the operator to input commands and make adjustments to the machine’s settings and parameters.
By ensuring the proper functioning and interaction of the display unit and control panel, operators can monitor and control their CNC milling machines for optimal performance and precision. These components play a vital role in the overall operation of the CNC milling machine, allowing the operator to achieve the desired level of accuracy and consistency in the final machined product.
Customizing CNC Machining for Specific Needs
A key factor in customizing CNC machining involves making a choice between manual machining and CNC precision, taking into account factors such as:
- Accuracy
- Time
- Technical experience
- Labor
- Production rate
- Cost
By carefully considering these factors and adjusting the machining process accordingly, operators can achieve the desired level of customization and precision for their specific needs.
Adjusting for Complexity: Manual Machining vs. CNC Precision
- Holes
- Slots
- Grooves
- Pockets
These features can be created on any surface of the workpiece.
Conversely, manual machining offers flexibility and adaptability to unique or complex part geometries, making it a viable option for certain projects. By understanding the unique requirements of each project and adjusting the machining process accordingly, operators can achieve the optimal level of customization and precision for their specific needs.
CNC Milling in Action: From Raw Material to Machined Part
Through a series of precise and accurate cuts made by a spinning cutting tool, the CNC milling process converts raw material into finished machined parts. The CNC mill is programmed to move the tool through the raw material, creating intricate shapes and designs that meet the desired specifications.
Each component of the CNC milling machine plays a role in achieving these precise and accurate results. The core components, axes, tools and attachments, and secondary components all work together to ensure that the CNC milling process delivers the desired level of precision and accuracy in the final machined product. By understanding the roles and functions of each component, operators can optimize their CNC milling machines for maximum precision and effectiveness.
Summary
In conclusion, CNC milling machines combine a range of components and systems to achieve unparalleled precision and accuracy in the manufacturing process. From the core components and axes that control the cutting tool’s movement to the supporting elements that provide stability and control, each aspect of the CNC milling machine plays a crucial role in achieving the desired results. By understanding these components and their functions, operators can optimize their CNC milling machines for maximum precision, efficiency, and effectiveness, creating intricate and accurate parts tailored to their specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 7 major parts of a milling machine?
Milling machines consist of seven major components: the column, knee, saddle, table, ram, head, and their associated components.
Why is CNC milling so expensive?
CNC Milling machines are more expensive due to their complex components, higher maintenance costs and precision engineering. The complexity of the machine increases the cost, as does the level of required capability. As a result, industrial CNC milling machines can be expensive to operate.
How do the X, Y, and Z-axes contribute to the precision of a CNC milling machine?
The X, Y and Z axes of a CNC milling machine are integral to its precision, as they control the movement of the cutting tool and workpiece, enabling precise and accurate machining.
What role do tools and attachments play in CNC milling?
Tools and attachments are essential for CNC milling, as they enhance the machine’s precision and efficiency, ensuring accurate machining results.
How can CNC machining be customized to meet specific requirements?
CNC machining can be customized by taking into account design, material selection, tool selection, and design optimization to meet specific requirements.