Services
Are you looking for a professional prototyping service to help actualize your ideas and assist with product development? Then you’ve come to the right place. 3ERP provides excellent quality, quick turnaround, and cost-effective rapid prototyping services to customers across the world. Equipped with cutting-edge prototyping and production manufacturing technology, advanced industrial-grade equipment, and an expert team of engineers, 3ERP can bring your idea from design to the market in just a few days. We’re excited to start working with you! If you have finished prototyping and are ready to move forward to production, please take a look at our low volume manufacturing service. Here are the main rapid prototyping processes we offer:
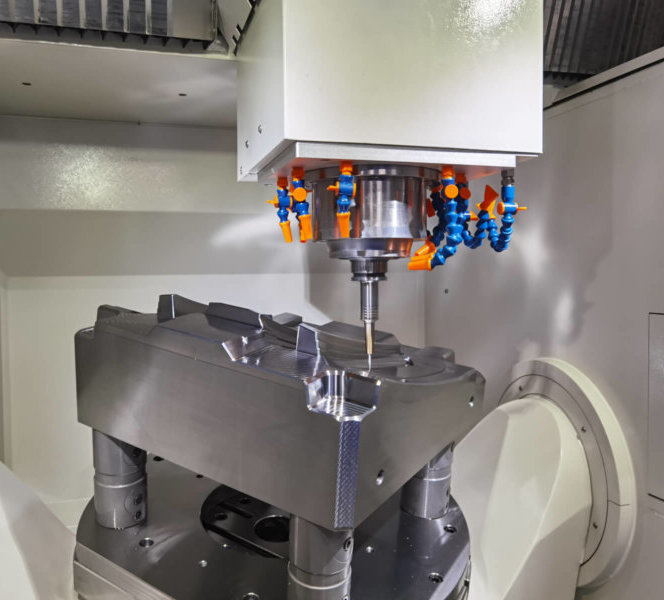
Rapid CNC machining
3ERP operates a large number of CNC machining centers, mills, and lathes (for CNC turning), enabling rapid prototyping of CNC machined parts made from plastic or metal. We offer a wide range of material and finishing options and the potential to combine CNC machining with other rapid prototyping processes.
CNC machining is one of the most high-precision rapid prototyping technologies available. Although rapid CNC machining prioritizes short turnarounds over ultra-tight tolerances, the quality remains high.
Turnarounds are fast in low volumes, and CNC prototyping produces parts not too far from production quality. The cost is higher than 3D printing but the surface finish and part strength are often superior.
- CNC Milling — Milled prototype & production parts in plastic and metal
- CNC Turning — All types of round components
- CNC Grinding — Tight tolerance and good surface
- CNC EDM — For deep pocket & sharp conners.

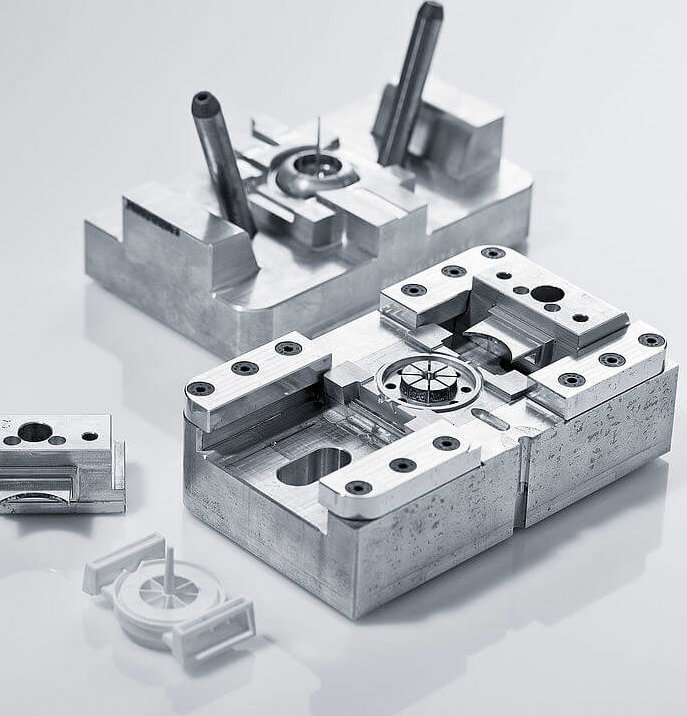
Rapid tooling
Rapid tooling (bridge tooling or prototype tooling) refers to the rapid CNC machining of metal tooling for injection molding. It is therefore the first step toward rapid injection molding.
Prototyping tooling for molding is ideal when the customer requires between 100–2,000 units of their injection molded parts; more than this and production-level steel tooling may be preferred.
Advantages of rapid tooling include fast turnarounds and the ability to carry out prototyping and testing of injection molded parts that might otherwise take months to produce. Rapid tooling is also significantly cheaper than mass production tooling.
Although rapid tooling and rapid injection molding is more expensive than 3D printing, it provides plastic parts much nearer to production quality that can therefore be used for functional testing.
- Plastic Injection Mold
- Die Casting Mold
- Extrusion Mold

Casting is generally considered a production process for high-quality metal parts, but rapid metal casting — using 3D printing to make low-cost patterns — offers an affordable route for prototyping cast metal.
3ERP’s rapid metal casting services are only available due to our close relationship with several large casting companies which typically would not accept low-volume (10+) prototyping orders from new customers.
Advantages of rapid metal casting include near production-quality metal parts, with potentially very large sizes, at surprisingly fast speeds. Cast parts also have excellent tensile strength and can also be post-machined.
- Pressure Die Casting
- Investment Casting
- Gravity Casting

See why our customers love us

We ordered a batch of plastic and metal prototypes from 3ERP recently. The package arrived two days earlier than promised. Our team was so excited after unpacking the order and seeing the parts: the surface finishes included painting, silk-screening, anodizing and laser engraving, which were so nice and detailed. Assembly was also very simple for us, since the parts are very accurately made. Great Job! We will definitely order our upcoming rapid prototyping projects from 3ERP.

If you are looking for rapid prototyping service, 3ERP is the best place to go. That’s from our years of experience working with them. 99.99% of time, they manage to get the job done perfectly in one go. The only thing we would dispute is their pricing, which is not the best, to be honest. But we did try to test out a couple of other rapid prototyping companies, and in the end we found it was better to stick with 3ERP. Considering the quality and services, they are the best value for the money for what we paid.
Why choose our rapid prototyping services?
Excellent. Efficient. Economic.
These three values define 3ERP’s rapid prototyping services. Working closely together, we can bring your product vision to reality in a few days, at a fair price.

No MOQ
We are flexible for one-off prototypes and low-volume parts. No matter the size of your order, we can handle it.

Competitive Pricing
We have built up an efficient rapid prototyping system which allows us to offer competitive prices that can match any offer.

Rapid Turnaround
Our capacities allows us to finish your rapid prototyping projects in days.

Experienced Engineers
Our team has years of experience in a wide range of industries and can handle even the most challenging projects.

Tight Tolerances
We service the aerospace and medical industries and can produce precise parts with tight tolerances.

Wide Range of Materials
We serve a wide range of clients and can offer a variety of rapid prototype materials and finishes.
Rapid Prototyping in Multiple Materials
When outsourcing your rapid prototypes, it is important to find a reliable rapid prototyping company that can handle range of materials, in order to keep the whole rapid prototyping project in one place. 3ERP is an ideal option in this regard. We can fabricate your prototype parts in plastics, metals and ceramics.

Plastics
A plastic prototype made by 3D printing, urethane casting, or CNC machining is the most common and economic way to review the appearance and function of your design.
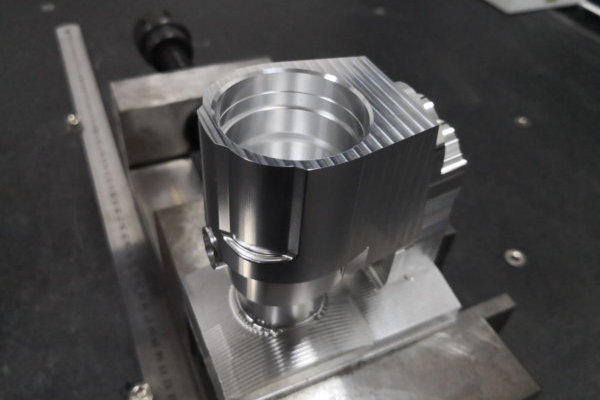
Metals
Metal prototypes and parts are usually made by CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, metal 3D printing or a casting process. Common metals include aluminum, magnesium, steel, brass, copper, etc.
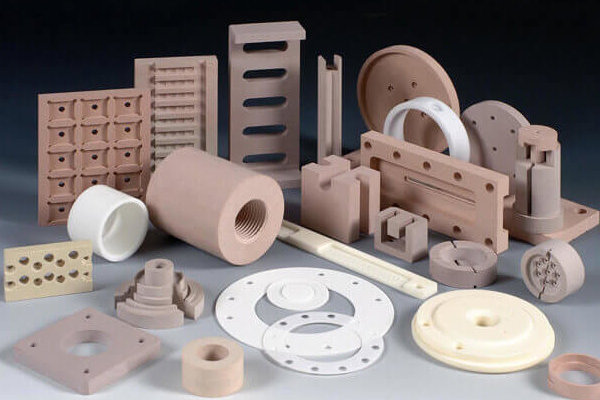

Ceramics
The advantages of ceramics in rapid prototypping are their extreme rigidity, insulation, and temperature resistance. They are popular in many industries because of this. We can offer Alumina, ZrO2, AIN, Si3N4 & SiC.
Prototypes and Parts Delivered Fast with 4 Simple Steps

Upload a CAD File

Quote & Design Analysis

Order Confirmation
Parts Are Shipped
What is rapid prototyping?

In simpler terms, you use technology to transform a product idea into a physical model.
This early physical model is a prototype. You’ll then refine this until you get the final version right. At that point, you’re ready to use or sell this into a product. So the faster you produce and refine your prototypes, the faster you can start going to market.
All rapid prototying jobs begin with digital models, but manufacturing hardware can range between CNC machining, 3D printing, and more.
You can make rapid prototypes from any material that’s compatible with the manufacturing hardware that you use. This might or might not include surface finishing treatments.
As its name implies, rapid prototyping puts an emphasis on fast turnarounds. Because when you want to develop and ship a product using rapid prototyping services, faster is always better.
Types of rapid prototype
Used by customers across many industries, rapid prototyping encompasses different technologies and materials. It also covers different kinds of prototype, including visual-only prototypes and functional prototypes used for testing a part’s performance.
- Concept model: A proof-of-concept prototype is the earliest and simplest kind of prototype, used to convey the basic idea of the part. Concept models are typically kept internal and may go through several iterations.
- Display prototype: A display prototype (or looks-like prototype) is a more developed prototype with a focus on its cosmetic aspects. The prototype should resemble the final part as much as possible, though it may not function fully or at all.
- Functional prototype: A functional prototype is built to behave like the end-use part. This enables the designer to carry out any necessary mechanical testing on the prototype to ensure its correct function.
- Pre-production prototype: A pre-production prototype or factory sample is the last kind of prototype used before production. It is typically used to validate the chosen mass manufacturing process, ensuring that the manufactured part will perform as expected.
Why get rapid prototypes?
Whether you are an engineer, industrial designer, or part of a product development team, rapid prototyping services can offer you distinct advantages such as:
- The ability to explore and realize concepts in a quick and cost-effective manner. Quick turnaround times and low costs allow teams to move far beyond the visualization of an idea, making it easier to grasp the properties and design of a product in the physical world.
- Reiterate designs and incorporate changes that allow for improved evaluation and functional testing of the product. This iterative rapid prototyping process provides a roadmap to developing and refining the final product before taking it to the market, ensuring that your design is optimized and foolproof.
- The ability to physically showcase concepts concisely and effectively. Rapid prototyping takes ideas, images and concepts from an idea or two-dimensional visual into hands-on products that clients, colleagues and collaborators can hold in their hands and see in action.
- The ability to thoroughly test and refine a concept. Being able to minimize design flaws with a small-volume rapid prototype run helps eliminate costly design flaws that might not be evident during an early assessment.
- By using a rapid prototyping service, you can save time and money by eliminating the need for setup and tooling. Since 3ERP can use the same equipment to produce various prototypes with different properties and materials, the overall costs and turnaround time of our rapid prototyping services are kept to a minimum.
Which rapid prototyping process is the best? Every coin has two sides.
Here are the pros and cons!
Find out the best way to make your project
How to get your prototypes done
Using rapid prototyping technologies requires design software. This software allows you to design a part on a computer, controlling its shape and dimensions and making design adjustments based on the chosen manufacturing technique.
However, whether you are able to develop a feasible digital design probably depends on your level of design and engineering experience.
Those without prior CAD experience might need to consult a professional product designer to fulfill the design brief. Professionals know how to manipulate the software, and they also know whether a design can realistically be fabricated using hardware like a CNC machine. (We often receive designs that are not manufacturable because they do not take into account factors like draft angles, parting lines and overhangs.)
Those who do have CAD experience — product designers, R&D specialists, etc. — can create a digital design using their design suite of choice then export it to a machine-readable format such as a STEP file (for CNC machining, etc.) or a Mesh file (for 3D printing etc.).
The digital file is the most important stage, but you must also specify a desired material, quantity and surface finish (if required) to the rapid prototyping company.
In many cases, you might prefer to send off Requests for Quotation (RFQs) to several rapid prototyping companies in order to compare quotations in terms of price, proposed lead time and the reputation of the manufacturer.
Once a satisfactory quotation has been received, you can finalize the order with the rapid prototyping company, who will use your digital design and order specifications to commence production.
The prototypes will be shipped to you once production is complete.
Rapid Prototyping: Case Studies
Rapid Prototyping FAQ
Why use rapid prototypes?
Rapid prototyping is a fast way to verify the aspect and function of your design. Prototypes are also widely used for business proposals, where they can be shown to potential investors and customers.
How fast can I receive my prototype parts?
Most rapid prototyping projects can be completed in a matter of days, and we offer fast global delivery. If you require a precise lead time, please submit your project to get a free quotation and lead time information at the same time.
What materials are available for rapid prototyping?
3ERP does rapid prototyping of parts in a wide range of plastic and metal materials, and we have listed common materials for each prototyping process. Check our individual service pages for more details. If you don’t see your required material, get in touch with our team.






