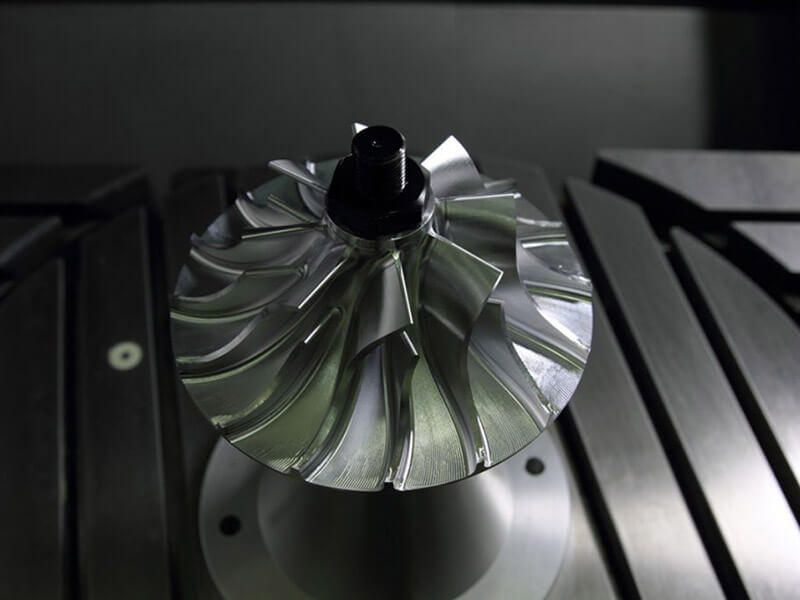
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that produces strong and durable parts in giant quantities. It is one of the most cost-effective manufacturing processes and works with a wide array of plastic materials, including thermoplastics and thermosets. You can even mold plastic components over other materials using overmolding and insert molding.
Sometimes, however, typical injection molding plastics will not suffice for a part that demands greater strength, durability, or stiffness, and this can make it tempting to use a metal manufacturing process instead of a plastic process.
Fortunately, there is a simpler alternative within the realm of injection molding. By using fiber reinforced or fiber-filled resins, it is possible to make stronger parts without resorting to metals or an alternative manufacturing process.
Fiber composite materials possess excellent material properties, and many of them can be manufactured just like ordinary injection molding plastics.
What is a fiber-reinforced / fiber-filled material?
In injection molding, fiber-filled materials are plastic resins mixed with glass fibers, carbon fibers, silicon fibers, ceramic fibers or natural fibers. These fibers — which are spread more or less evenly throughout the plastic matrix — can be long or short, and they provide advantages such as toughness, strength and a high specific modulus.
Plastics mixed with fibers in this way are known as bulk molding compounds. Glass fibers are the most widely used in compounds for IM, and can be mixed with plastics like polyamides (nylons) and polycarbonates.
But materials with added fibers are also used in other manufacturing processes besides injection molding. In fact, the molten plastic used in injection molding is not an ideal repository for, e.g. carbon fibers, for which a uniform direction of fibers is needed to make truly strong parts.
With the injection molding process, you cannot control the orientation of fibers when they are mixed into liquid resin, because they end up simply floating within the plastic matrix. For glass fiber-filled parts, this random orientation of chopped fibers still results in strong and useful parts, but it is not a particularly effective use of carbon fibers, which are very expensive and better used in other ways.
Creating continuous fiber-reinforced parts — where fibers are oriented in the same direction for maximum strength — is easier with processes like extrusion or some new forms of additive manufacturing, where the fibers can be easily oriented.
That being said, it is possible to achieve fiber-reinforced molded parts by lining a mold with a fiber-reinforced fabric then injecting resin into the cavity.
What are the fiber materials used for?
Injection molding with fiber-filled materials or fiber-reinforced materials can produce parts suitable for many industries. At present, common applications include automotive and aerospace, particularly with regard to lightweight, as well as architectural and industrial parts.
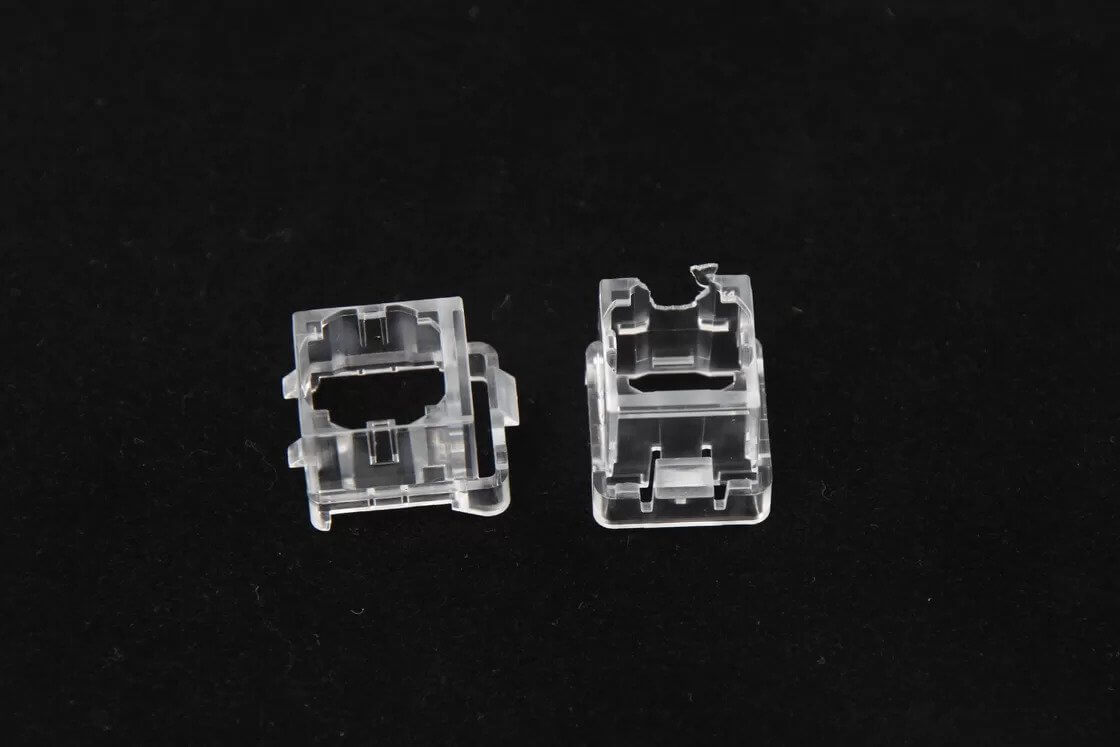
Glass-filled plastics can be used as a metal substitute, with parts such as nuts and bolts, brackets and levers.
Most common injection molding composites used by 3ERP:
Glass-filled polyamide
- High stiffness, wear resistance, creep resistance and surface quality
- Used in automotive, industrial, electrical, electronics
- Suitable for automotive parts like engine covers, engine parts, etc.
Glass-filled polycarbonate
- High tensile strength, stiffness, toughness
- Used in automotive, electrical, mechanical engineering
- Used as a replacement for metals like aluminum and zinc
Glass-filled PET (PBT GF30)
- High mechanical strength, dimensional accuracy, and corrosion/water resistance
- Used in automotive, electrical, mechanical engineering
- Suitable for parts like cogs, bearings and wear plates
Glass-filled PPS
- Very high rigidity, high strength, and flame retardance
- Suitable for parts that undergo high thermal stress, precision parts, etc.
The ratio of plastic to fiber also determines the possible uses and applications of composite fiber material. For example, glass-filled polyamide may contain 10%, 20%, 30%, or more than 30% glass fibers.
A recent report from MarketsandMarkets found that the most widely used mix of nylon and glass fiber is the 30% variety, which is often used in the automotive industry because of its high strength and rigidity.
Fiber-filled parts from 3ERP
3ERP offers plastic injection molding services using fiber-filled materials for high-quality parts in any quantity. And combined with our rapid tooling services, we can deliver injection molded parts to meet tight deadlines.
We also make fiber-filled parts using other processes. For example, we can make CNC machined parts and prototypes from glass-filled polyamide or polycarbonate.
Contact us today for a free quote on your next project for fiber-filled or fiber-reinforced parts.