As we stand at the crossroads of technology and creativity, a paradigm shift is palpably reshaping how we design and create. Nestled at the heart of this revolution is a powerful tool that has radically changed the face of multiple industries: Computer-Aided Design (CAD).
But what exactly is this much-discussed tool, and why all the fuss about it? This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about CAD, from its inception and benefits to its implications in various fields.
What is Computer-Aided Design?
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) refers to the use of computer systems to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. Put simply, CAD is a type of software that allows engineers and designers to create products, technical drawings, and models on a computer rather than a drawing board.
Modern CAD packages can also frequently let an operator approaches design in a different manner, producing three-dimensional, solid volumes or surface models, instead of two-dimensional projected views. As a result, computer-aided design has become an especially important technology that engineers, architects, and even fashion designers employ in their design processes.
Short History of Computer-Aided Design
The history of computer-aided design dates back to the 1960s when engineers used it as a drafting tool. Back then, CAD systems were high-speed, standalone mainframes that were not user-friendly and were only used for very specific applications.
However, with the evolution of computers and technology, computer-aided design transformed from a basic drafting system into a more robust and intuitive design tool. Today, it’s used for a wide range of applications, from conceptual design and layout of products to definition of manufacturing methods of components.
What are the Different Types of Computer-Aided Design?
The world of CAD is expansive and offers a broad spectrum of tools to cater to various design needs. Below are some of the most common types:
2D CAD
Two-dimensional, or 2D CAD, involves creating flat, two-dimensional drawings composed of lines, circles, and curves. 2D computer-aided design is generally used for architectural blueprints or engineering layouts.
3D CAD
Three-dimensional CAD, or 3D CAD, is more advanced and involves the creation of solid objects in a three-dimensional space. 3D CAD allows engineers and architects to view and manipulate their designs from different angles, giving them a better understanding of how the final product will look and function.
Freeform CAD
Freeform CAD tools allow for the design of complex and unconventional shapes that may not be possible with traditional 2D or 3D CAD tools. This type of computer-aided design is frequently used in the fashion and entertainment industries for tasks such as designing clothing or creating CGI characters.
Where is Computer-Aided Design Used and Industries that Utilize it?
CAD is employed in a wide range of industries, from architecture and engineering to fashion design and entertainment. This technology has become a cornerstone for many businesses, enabling them to streamline their design processes and produce more detailed and accurate designs.
Engineering Projects
Engineering projects heavily rely on CAD software. Engineers use CAD for creating designs and technical drawings of machinery, systems, and infrastructure. For example, CAD is employed in designing automotive parts, bridges, tunnels, and even in aerospace technology for designing aircraft and space vehicles.
It allows engineers to manipulate designs in three dimensions (3D), analyze them from every desired angle, and identify interference or errors. It also enables the creation of two-dimensional projected views or ‘drawings’ from the 3D models for the final engineering drawing views.
Architecture and Interior Design
CAD plays a pivotal role in both architecture and interior design. Architects use it to create detailed architectural designs, from conceptual design to layout, and the final draft. The designs are not just limited to the building’s exterior but also include intricate interior design details.
Interior designers use CAD to optimize space, experiment with different layouts, and visualize the final look in 3D before the physical implementation begins. The CAD model becomes a valuable communication tool between architects, interior designers, and clients.
Manufacturing and Product Design
Computer-aided design significantly influences the manufacturing industry, radically changing traditional manufacturing methods. It enables the generation of accurate 3D models of product designs, which serve as a digital prototype before the actual manufacturing begins. CAD’s precision helps in identifying possible design flaws, thereby lowering product development costs. Moreover, CAD facilitates rapid prototyping, reducing the need for costly physical prototypes.
In the realm of product design, CAD proves crucial for a multitude of objects. From creating complex electronic devices to simple furniture pieces, CAD makes it all seamless. Even industries like jewelry and fashion have embraced CAD to create intricate designs.
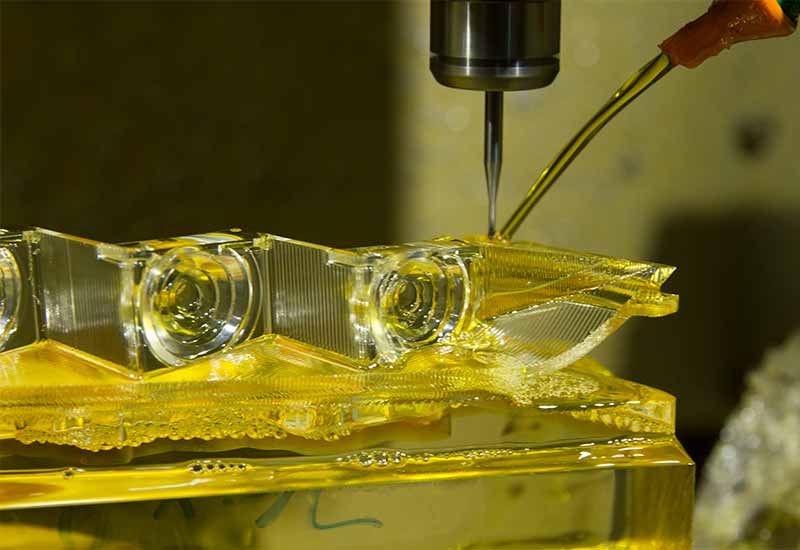
CNC Machining
In the world of machining, CAD becomes an essential tool that dramatically enhances efficiency and precision. This industry focuses on creating parts by removing material from a workpiece, involving processes such as drilling, milling, turning, and grinding. These tasks, which may be complex and time-consuming when done manually, are significantly simplified through the use of CAD.
Machinists use CAD software to develop intricate designs and technical drawings of parts that need to be produced. The CAD system helps in visualizing these parts in three dimensions, facilitating a thorough understanding of their geometry and features before the machining process begins. This visualization is crucial in planning the manufacturing process, deciding the cutting paths, and selecting appropriate tools and fixtures.
Moreover, computer-aided design supports the creation of accurate digital prototypes that mimic real-world objects, including the smallest details of their form and geometry. By simulating the cutting process, machinists can identify potential issues, optimize designs, and eliminate costly mistakes.
In a broader context, CAD forms an integral part of Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM). Designs created through CAD can be seamlessly integrated into CAM systems. These systems then generate G-code, a language that instructs CNC machines (computer numerical control machines) on how to cut the real-world objects.
In essence, computer-aided design acts as the blueprint for CNC machining, paving the way for high-speed, high-precision manufacturing with lower production costs and less waste. This advanced application of CAD solidifies its position as an essential tool in modern manufacturing.
Education and Training
Many educational institutes offer CAD certificate programs that equip learners with the skills necessary to work with CAD systems effectively. Students pursuing an associate or bachelor’s degree in engineering, architecture, and similar fields often find CAD training to be an essential part of their curriculum.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, CAD is used to design every component of a vehicle, from the bodywork to the engine parts. This allows manufacturers to test and modify designs before a physical prototype is created, thus saving time and money.
Fashion Industry
The fashion industry also reaps the benefits of CAD by creating digital prototypes of clothing designs. These virtual models can be altered and tested for various materials and cuts before any physical components are produced.
What are the Benefits of CAD over Traditional Sketching and Manual Drafting?
The advent of CAD has redefined traditional sketching and manual drafting, bringing a plethora of advantages. Here are a few:
- Accuracy and Precision: CAD tools offer a level of detail and precision that is hard to match with manual drafting. They allow the user to zoom in and modify the design to the smallest detail, leading to a higher quality final draft.
- Efficiency and Productivity: With CAD, design changes and updates can be executed swiftly, without having to start from scratch as in manual drafting. This increases productivity by saving time and resources.
- 3D Visualization: Unlike manual drafting, CAD provides the ability to create and manipulate 3D models. These 3D models offer a better understanding of the design, including a realistic visualization of the final product.
- Error Reduction: CAD software comes with features that automatically check for inconsistencies, design flaws, or errors in the model, significantly reducing the chance of mistakes.
- Ease of Sharing and Collaboration: CAD files can be easily shared and accessed across different platforms, making it easier for teams to collaborate. Digital files also simplify the process of maintaining, tracking, and updating design documents.
What are the Most Popular CAD Softwares and Tools?
As the demand for CAD has grown, so has the availability of software packages. Here are some of the most popular CAD software and tools:
- AutoCAD: Developed by Autodesk, AutoCAD is one of the most widely used CAD tools, offering powerful features for 2D and 3D design and drafting.
- SolidWorks: Known for its user-friendly interface and robust features, SolidWorks is primarily used for mechanical design but also supports other types of designs.
- CATIA: Developed by Dassault Systems, CATIA is known for its advanced surface modeling capabilities, widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- Revit: Also developed by Autodesk, Revit is specifically designed for building information modeling (BIM), allowing architects and engineers to design and manage building projects.
- SketchUp: An intuitive tool popular among architects and interior designers, SketchUp is known for its ease of use in creating 3D models.
Are There Any Disadvantages of Using CAD?
While CAD brings numerous benefits to the table, it’s not without its drawbacks. One of the most frequently cited disadvantages is the cost. High-end CAD software can be expensive to purchase and maintain. Also, the hardware needed to run these programs efficiently can also entail a significant investment.
Learning CAD can also be challenging. While some basic CAD software is user-friendly, more advanced systems can have steep learning curves. Professionals may require extensive training to master these tools.
Additionally, over-reliance on CAD could potentially stifle creativity. As designs are constrained by the capabilities of the software, designers may find their creativity limited by the tool rather than enhanced by it.
What are the Skills Required for CAD?
Mastering CAD requires both technical skills and a strong understanding of the field in which it’s being applied. Here are some key skills:
Is CAD Hard to Learn?
The complexity of learning CAD largely depends on the software and the individual’s background. Basic CAD software can be learned in a few weeks of dedicated study and practice. However, more advanced software, especially those used for specific industries like mechanical engineering or architecture, may require months of training.
Are There CAD Certificates?
Yes, numerous educational institutions and software companies offer CAD certificate programs. These programs typically cover fundamental concepts, software tools, and real-world applications of CAD. Certifications can demonstrate a level of competency and professionalism in computer-aided design and are often favored by employers.
The top 5 CAD certifications, based on their popularity and industry recognition, are:
- Autodesk Certified Professional (ACP): This certification is highly regarded and covers a wide range of Autodesk software, including AutoCAD, Revit, and Inventor. Autodesk is a leading provider of CAD software, making this certification highly valuable in the industry.
- SolidWorks Certification: SolidWorks is widely used in various industries, and its certification programs, such as the Certified SolidWorks Professional (CSWP) and Certified SolidWorks Associate (CSWA), are highly respected. These certifications validate skills in 3D modeling, assembly design, and drawing creation using SolidWorks software.
- Siemens PLM Software Certification: Siemens offers certifications for their CAD software solutions, including NX and Solid Edge. Siemens PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) software is widely used in industries like automotive and aerospace. These certifications demonstrate proficiency in using Siemens PLM software for design and engineering tasks.
- CATIA Professional Certification: CATIA, developed by Dassault Systèmes, is extensively used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing. The CATIA Professional certification is highly valued and validates expertise in using CATIA for design and engineering purposes.
- Certified PTC Creo User: PTC Creo is a powerful CAD software used for product design and development. The Certified PTC Creo User certification confirms proficiency in using Creo for tasks like part modeling, assembly design, and drawing creation.
What are the Differences Between CAD and CAM?
CAD and CAM are two technologies often used together in the design and manufacturing industries. While they both play crucial roles in these sectors, they serve different purposes.
CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, as we’ve explored, involves using computer software to create, modify, analyze, or optimize a design. It is predominantly used in the design stage of a product’s lifecycle, turning conceptual design into detailed, technical drawings and 3D models. It ensures that designs are precise, amendable, and ready for production or construction.
On the other hand, CAM, which stands for Computer-Aided Manufacturing, is the use of software and computer-controlled machinery to automate manufacturing processes. It is typically used after the design phase. CAM software takes the design data from CAD software and uses it to control the machinery that creates the final product. It facilitates the manufacturing process by providing detailed instructions to CNC machines about how to make the product.
In summary, while CAD is about designing the product, CAM is about making the product.
What are Future Trends in CAD?
As we look towards the future, CAD is poised for exciting developments. Here are some trends we expect to shape the CAD landscape:
- Cloud-Based CAD: As with many other software applications, computer-aided design is moving towards the cloud. Cloud-based CAD allows for better collaboration, easier access to designs from anywhere, and lower costs as it eliminates the need for expensive hardware and continual software upgrades.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are set to play a substantial role in CAD. These technologies can automate routine design tasks, identify design patterns, and even suggest design improvements, making the design process more efficient and intelligent.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR can provide immersive design experiences, allowing designers to visualize and interact with 3D models in a more realistic environment. They can also be used to present designs to clients in a more engaging and understandable way.
- Generative Design: This is a design method where the designer inputs goals and constraints into the CAD software, and the software uses algorithms to generate optimal design options. It allows designers to explore a wide range of design possibilities quickly and can lead to innovative solutions that a human designer might not consider.
Conclusion
Computer-Aided Design is a crucial technology used in various industries, including engineering, architecture, and fashion design. It allows designers to create precise and detailed technical drawings, simulate designs, and create digital prototypes. Though learning and mastering CAD software can be challenging, the benefits it offers in terms of accuracy, efficiency, and design quality make it a valuable skill for any design professional.
From humble beginnings as a tool to simplify drafting, computer-aided design has evolved into a complex, intelligent system integral to modern design and manufacturing processes. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of CAD are set to grow even further, enhancing the design process and contributing to the creation of better, more innovative products. Whether you’re a budding designer, an experienced engineer, or simply someone interested in the intersection of design and technology, understanding CAD is sure to be a valuable asset in today’s digital age.